PHP variables are like containers used to temporarily store data and use it during program execution. In PHP, using variables allows you to store values and easily perform operations such as calculations and string manipulation. This article provides a detailed explanation of PHP variables.
1. Basics of Variables
To define a variable in PHP, use the dollar sign ($).
$greeting = "Hello, World!";
$number = 42;Variable Rules
- Variable names must start with
$. - Variable names can use alphanumeric characters and underscores (
_). - Variable names cannot start with a number.
- Variable names are case-sensitive.
2. Data Types of Variables
PHP variables are dynamically typed, meaning their type is determined automatically based on the value. Main data types include the following:
Scalar Types (single value)
- String
$string = "This is a string."; - Integer
$integer = 100; - Float/Double
$float = 3.14; - Boolean
$bool = true;
Compound Types (multiple values)
- Array
$array = ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange"]; - Object
class Person { public $name; function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } } $person = new Person("Taro");
Special Types
- NULL (state where variable is undefined or has no value)
$nullVar = NULL; - Resource (used for special resources like database connections)
$file = fopen("test.txt", "r");
3. Variable Scope
In PHP, variables have a defined scope (the range where they can be used).
Global Variables
Variables defined outside of functions cannot be used directly inside functions. However, using the global keyword makes them accessible inside functions.
$globalVar = "Global variable";
function testGlobal() {
global $globalVar;
echo $globalVar;
}
testGlobal();You can also use the $GLOBALS array to access global variables.
function testGlobalArray() {
echo $GLOBALS['globalVar'];
}
testGlobalArray();Static Variables
Static variables are variables that retain their value even when defined inside a function. Normally, local variables are re-initialized each time the function is called and are discarded after execution. By using the static keyword, the variable value is retained across function calls.
function counter() {
static $count = 0; // Initialize as static variable
$count++; // Increment on each call
echo $count;
}
counter(); // 1
counter(); // 2
counter(); // 3Output
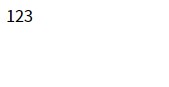
Why use static?
- To retain state
Useful when you want to retain results from previous calls. In this example, the count is maintained across calls. - Difference from global variables
You can retain state within the function without using global variables, avoiding unnecessary scope pollution. - To avoid recalculating every time
Ideal for functions that are called multiple times but require only one-time calculation.
4. Variable Manipulation
Checking Variable Types
PHP provides several functions to check the type of a variable.
var_dump($variable); // Output detailed variable info
is_int($variable); // Check if variable is an integer (returns true/false)
is_string($variable);// Check if variable is a string (returns true/false)var_dump()
A handy function that shows both the “type” and “value” of a variable. For example, it displays length and content for strings, and number of elements for arrays.
is_int() / is_string() etc.
is_XXX() functions return true / false based on type. Others include is_bool(), is_float(), is_array(), is_object(), etc. Use as needed.
Checking Variable Existence
isset($variable); // Check if variable is set
empty($variable); // Check if variable is emptyisset()
Checks whether a variable is defined and not null. Returns false if undefined or null, otherwise true.
empty()
Checks if a variable is “empty” (e.g., 0, “”, “0”, [], null, etc.).
Returns true if any of the following are true:
- Value is an empty string
"" - Value is 0 or “0”
- Value is null
- Array is empty
[] - Variable is undefined
- Boolean value is
false
If none apply, returns false.
Difference between isset() and empty()
- isset() checks if a variable exists and is not null.
- empty() checks if a value is empty (0, “”, [], null, false, etc.).
Deleting Variables
unset($variable); // Delete the variableunset()
Deletes the specified variable, making it no longer exist. Accessing it afterward may cause an error or warning. Re-defining with the same name will treat it as a new variable.
Summary
PHP variables play a crucial role in storing and manipulating data within programs. Understanding how to use and manage variables properly allows you to write more efficient code. Use this article as a reference to become comfortable handling PHP variables!
